Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
西内 満美子; 小倉 浩一; Pirozhkov, A. S.; 谷本 壮; 余語 覚文; 榊 泰直; 堀 利彦; 福田 祐仁; 金崎 真聡; 匂坂 明人; et al.
Proceedings of SPIE Europe Optics + Optoelectronics 2011, Vol.8079, 7 Pages, 2011/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Optics)レーザー駆動陽子線の特異な性質により、多くの応用の可能性がうたわれている。その中には、医療用の小型加速器がある。われわれの最終ゴールはここにある。そのために、レーザーを薄膜個体ターゲットに照射してイオン加速実験を行った。われわれのレーザーは、非常にコントラストが高い、短パルスの小型テーブルトップレーザーである。レーザーは800nm, 40fs, 4J, 10 のコントラスト、ピーク強度
のコントラスト、ピーク強度 10
10 Wcm
Wcm のパラメータを持ち、ターゲットとしては、100umからsub-umの厚みの固体ターゲットを用いた。その結果として、最高エネルギー14MeVの陽子線で、10MeV付近の個数が10Hzで10分間に、マウスの皮膚に2Gy照射するに十分なドーズ量を持つ陽子線の発生に成功した。
のパラメータを持ち、ターゲットとしては、100umからsub-umの厚みの固体ターゲットを用いた。その結果として、最高エネルギー14MeVの陽子線で、10MeV付近の個数が10Hzで10分間に、マウスの皮膚に2Gy照射するに十分なドーズ量を持つ陽子線の発生に成功した。
余語 覚文; 前田 拓也*; 堀 利彦*; 榊 泰直; 小倉 浩一; 西内 満美子; 匂坂 明人; Bolton, P.; 村上 昌雄*; 河西 俊一*; et al.
Proceedings of SPIE Europe Optics + Optoelectronics 2011, Vol.8079, 8 Pages, 2011/04
Human cancer cells are irradiated by laser-driven quasi-monoenergetic protons. Laser pulse intensities at the 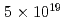 W/cm
W/cm level provide the source and acceleration field for protons that are subsequently transported by four energy-selective dipole magnets. The transport line delivers 2.25 MeV protons with an energy spread of 0.66 MeV and a bunch duration of 20 ns. The survival fraction of in-vitro cells from a human salivary gland tumor is measured with a colony formation assay following proton irradiation at dose levels up to 8 Gy, for which the single bunch does rate is
level provide the source and acceleration field for protons that are subsequently transported by four energy-selective dipole magnets. The transport line delivers 2.25 MeV protons with an energy spread of 0.66 MeV and a bunch duration of 20 ns. The survival fraction of in-vitro cells from a human salivary gland tumor is measured with a colony formation assay following proton irradiation at dose levels up to 8 Gy, for which the single bunch does rate is 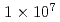 Gy/s and the effective dose rate is 0.2 Gy/s for 1-Hz repetition of irradiation. Relative biological effectiveness at the 10% survival fraction is measured to be
Gy/s and the effective dose rate is 0.2 Gy/s for 1-Hz repetition of irradiation. Relative biological effectiveness at the 10% survival fraction is measured to be 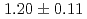 using protons with a linear energy transfer of
using protons with a linear energy transfer of 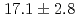 keV/
keV/ m.
m.
前田 拓也; 余語 覚文; 出水 祐介*; 堀 利彦; 榊 泰直; 巴 悠介*; 近藤 公伯; 村上 昌雄*
no journal, ,
The Hyogo Ion Beam Medical Center (HIBMC) was established in May 2001, a leading project of the "Hyogo Cancer Strategy". As its major characteristic, both proton and carbon ion beams can be generated. The accelerator is a synchrotron that can accelerate proton and carbon ion beams at a maximum of 230 and 320 MeV/u, respectively. Three irradiation rooms installed with 45 , horizontal/vertical, and horizontal fixed ports can be used for carbon ion radiation biological experiment and therapy. Moreover laser technology to accelerate particle beam therapy, by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) advances development now aim to bring innovation to transform conventional treatment, and spread the particle beam therapy, taking advantage of the performance of particle beam therapy, proton therapy equipment laser driven activities are designed to achieve for clinical application to. We have so far, X-ray, proton, and carbon ion beam lines, the laser-driven proton ion beam, has been examined from the standpoint of comparative molecular cell biology of cancer cells to radiation effects. So far, considering the differences in the types of cytostatic effect and the effect of DNA cleavage and on the relevance of apoptosis studies in each lines irradiated cancer cells. In this presentation we reports on the difference of the irradiation effect in X-rays, the proton beam, and the carbon ion beam to the human cancer cell, and it applies on the focus to survival rate after the X-ray, synchrotron proton beam, the synchrotron carbon ion beam, and the laser driven proton is irradiated.
, horizontal/vertical, and horizontal fixed ports can be used for carbon ion radiation biological experiment and therapy. Moreover laser technology to accelerate particle beam therapy, by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) advances development now aim to bring innovation to transform conventional treatment, and spread the particle beam therapy, taking advantage of the performance of particle beam therapy, proton therapy equipment laser driven activities are designed to achieve for clinical application to. We have so far, X-ray, proton, and carbon ion beam lines, the laser-driven proton ion beam, has been examined from the standpoint of comparative molecular cell biology of cancer cells to radiation effects. So far, considering the differences in the types of cytostatic effect and the effect of DNA cleavage and on the relevance of apoptosis studies in each lines irradiated cancer cells. In this presentation we reports on the difference of the irradiation effect in X-rays, the proton beam, and the carbon ion beam to the human cancer cell, and it applies on the focus to survival rate after the X-ray, synchrotron proton beam, the synchrotron carbon ion beam, and the laser driven proton is irradiated.
Bolton, P.
no journal, ,
The primary goal of the Photo-Medical Research Center (PMRC) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency is developing an integrated, laser-driven ion accelerator system (ILDIAS) prototype for application to laser-driven ion beam radiotherapy (L-IBRT). PMRC pursues all-optical acceleration of protons to high kinetic energy ( 250 MeV) via intense laser-plasma interaction at the target site. The ILDIAS concept is presented along with some laser and proton beam delivery requirements for radiotherapy. The ILDIAS will necessarily be comprised of several subsystems that include at least: the laser, the target, instrumentation, ion transport optics and the delivery (to the patient). Toward our higher energy goal for L-IBRT we have achieved maximum proton energies near 14 MeV in single shot experiments and also demonstrated repetition-rated (1 Hz) transport of protons with energy up to 3 MeV. At about 2 MeV 5 nanosecond bunches have been transported at a flux level 106 protons/cm
250 MeV) via intense laser-plasma interaction at the target site. The ILDIAS concept is presented along with some laser and proton beam delivery requirements for radiotherapy. The ILDIAS will necessarily be comprised of several subsystems that include at least: the laser, the target, instrumentation, ion transport optics and the delivery (to the patient). Toward our higher energy goal for L-IBRT we have achieved maximum proton energies near 14 MeV in single shot experiments and also demonstrated repetition-rated (1 Hz) transport of protons with energy up to 3 MeV. At about 2 MeV 5 nanosecond bunches have been transported at a flux level 106 protons/cm with a 5% energy spread. Also for recent cell irradiation studies we transported 20 nanosecond bunches at 2.3 MeV with flux levels of order 107 protons/cm
with a 5% energy spread. Also for recent cell irradiation studies we transported 20 nanosecond bunches at 2.3 MeV with flux levels of order 107 protons/cm with a 30% energy spread. In this latter case human cancer cells received single bunch doses of 0.2 Gy. Typically we can expect the ILDIAS to produce single bunches of
with a 30% energy spread. In this latter case human cancer cells received single bunch doses of 0.2 Gy. Typically we can expect the ILDIAS to produce single bunches of  10 nanosecond duration with low duty factors in the range, 10
10 nanosecond duration with low duty factors in the range, 10 to 10
to 10 for 10 Hz and 100 Hz repetition-rate operation respectively.
for 10 Hz and 100 Hz repetition-rate operation respectively.